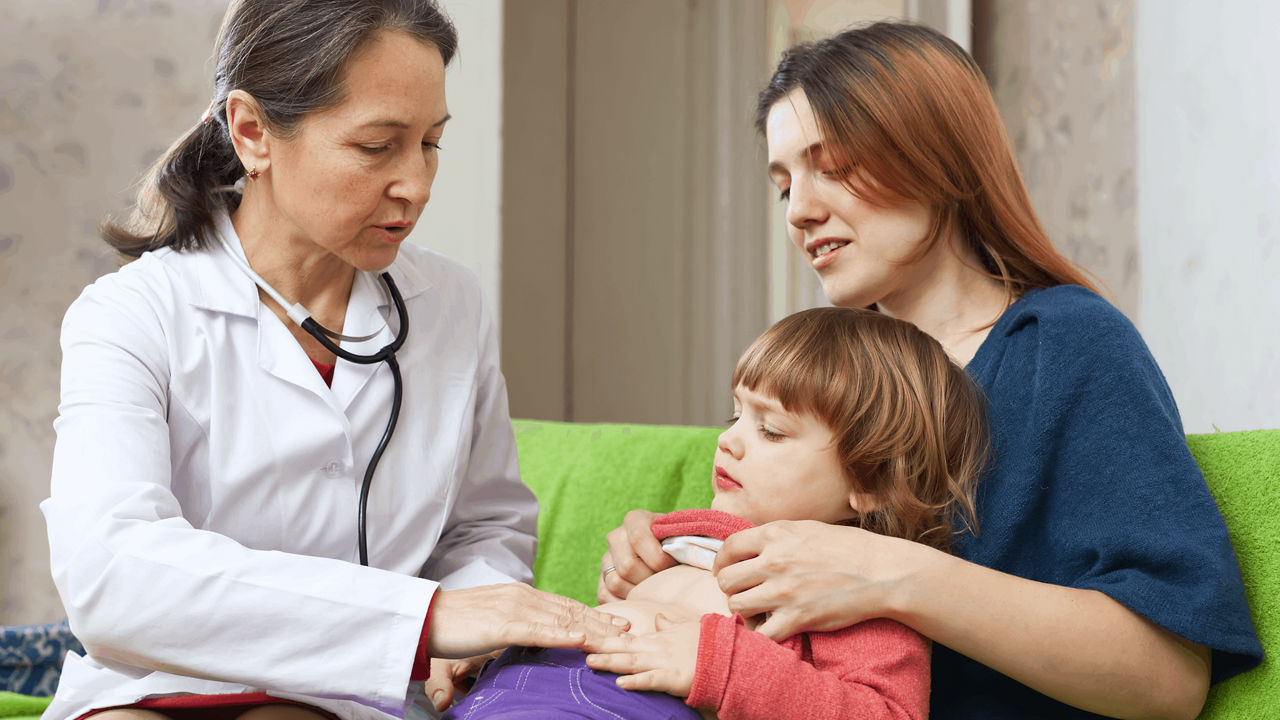
There are a number of reasons why some children can have difficulties growing optimally, including the presence of an underlying disease or condition such as cerebral palsy, congenital heart disease (CHD), cystic fibrosis, liver disease or cancer. Poor growth can have a detrimental effect on both short and long-term health outcomes.
Pediatric Disease Related Malnutrition (DRM)
Welcome to the healthcare professional pages of Pediatric disease related malnutrition (DRM), where you'll find more details on the topic, as well as relevant links to clinical guidelines, feature articles, including information about a new screening tool (Feeding Nutrition Screening Tool - FNST) that can help identify nutritional risk in children with cerebral palsy.
About medical nutrition
Normal growth for children starts with meeting their nutritional needs [1,2].
Appropriate growth starts with meeting children’s nutritional needs

For example, infants and children with CHD who have low weight pre-surgery are known to have poorer surgical outcomes or even have their essential surgery delayed3-5. Whether disease-related or not, chronic poor weight gain during early life is associated with long-term consequences, including stunting and permanent alterations in brain growth and function, leading to cognitive and behavioral impairment6-9. Appropriate growth and development start with nutrition, however achieving adequate nutrient intake can be challenging in this population – providing appropriate nutritional management solutions tailored to the child’s needs is essential to support their growth and development.
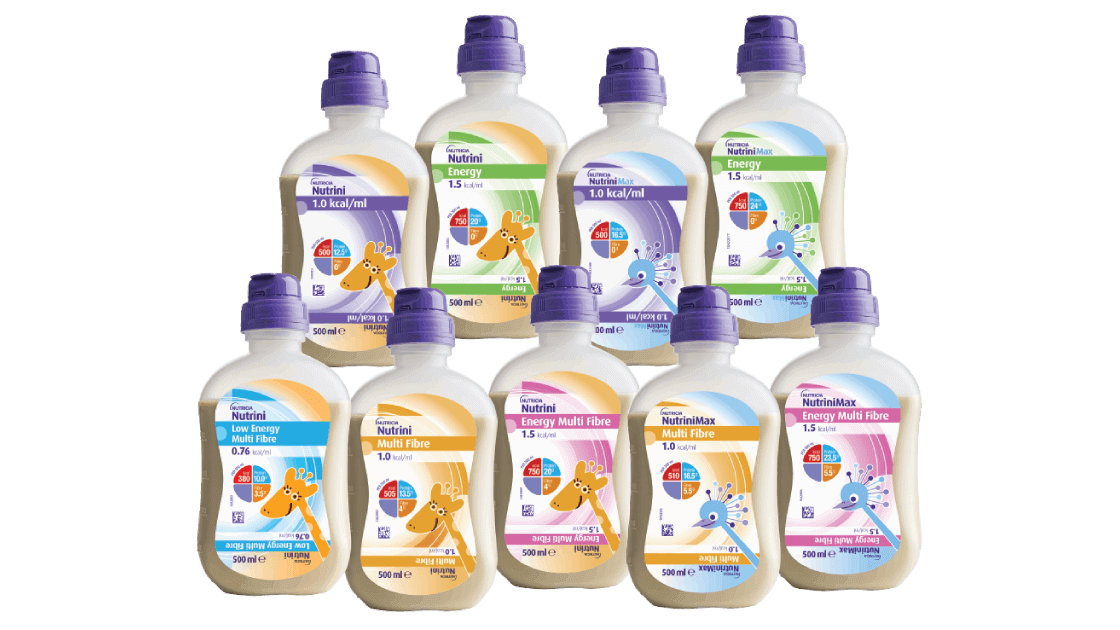
Pediatric DRM Portfolio
Our products play a key role during early life. From supporting healthy growth and development to providing the medical nutrition necessary when health is challenged including faltering growth. The Nutricia Pediatric DRM products on this page are foods for special medical purposes (FSMP) and intended for the dietary management of diseases and related medical conditions.

Pediatric DRM products
The Nutricia Pediatric DRM products must be used under medical supervision.
Clinical guidelines
Nutricia Education

Further educational resources
Get access to a central online hub to find the latest information relating to nutritional advances in pediatric disease-related malnutrition. Content includes webinars, infographics and podcasts.

Continued learning enables us all to deliver the best possible care to those who need it most. Here we bring science-led educational resources as well as news from leading medical congresses, helping to stay up-to-date with the latest advances in medical nutrition.
Patient story
Cath and Frankie’s story
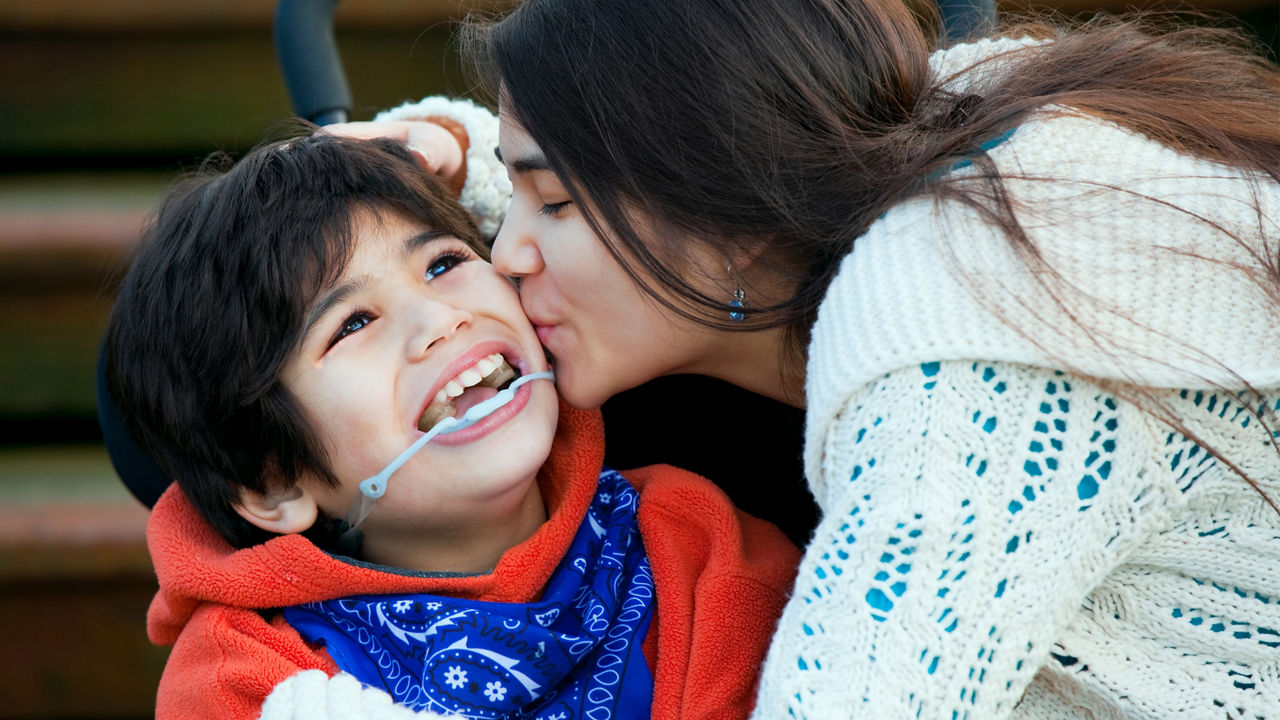
Frankie was born with a congenital heart disease, that was detected during his mother's pregnancy. At birth he was admitted into intensive care and has subsequently underwent numerous surgeries. Since it was difficult for Frankie to feed normally he struggled to gain weight and grow appropriately and was prescribed an enteral feed soon after birth. Now 4-years-old, Frankie is a bundle of joy and energy – he doesn't let anything stop him. Watch the video to find out more about Frankie's story.
Nutritional management of children with Cerebral Palsy
A third of children with cerebral palsy (CP) are undernourished10 which can have a negative effect on their health outcomes. Ensuring these children meet their required nutritional intake can be very challenging, especially for children with more complex needs11 and can put a burden on the quality of life of these families.

Feeding difficulties in children with cerebral palsy: why they matter and how to recognize them
Children with cerebral palsy often have difficulties with feeding and swallowing. These can cause children to become underweight and undernourished, with consequences for growth and development12,13. The Feeding and Nutrition Screening Tool14 can help parents screen for risk of feeding/swallowing difficulties and undernutrition quickly and easily, so they know when to seek medical help.
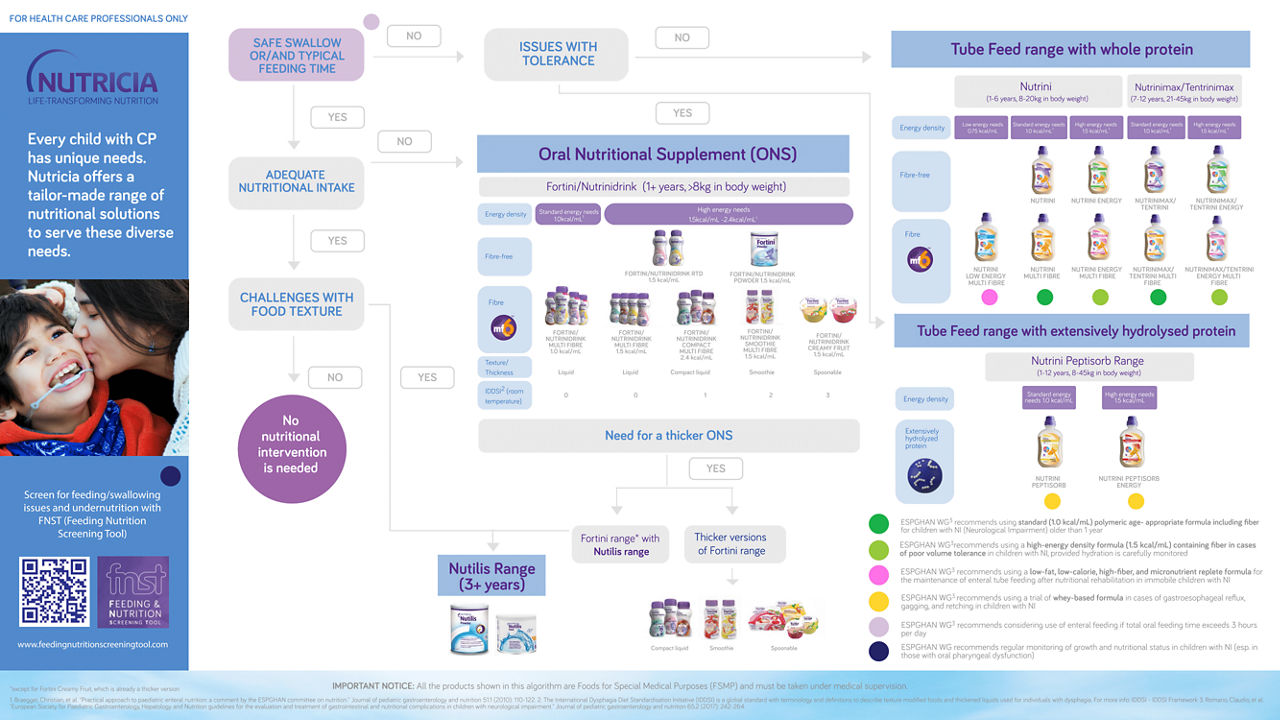
Support in finding nutritional solutions for children with Cerebral Palsy
Every child with Cerebral Palsy (CP) has different nutritional needs, including feeding time, ability to swallow, nutritional adequacy, and ability to tolerate. Click here for an interactive tool that supports finding the appropriate nutritional solution, following ESPGHAN guidelines.

Nutritional screening tool
Accurately measuring the nutritional status of these patients is essential to ensure these children get the nutritional intake they need to grow. That’s why Nutricia developed an online screening tool called the Feeding and Nutrition Screening Tool (FNST), the first scientifically validated online screening tool for early identification of feeding/swallowing difficulties and undernutrition in children with CP. By answering only four questions, this tool can help parents to identify risk of undernutrition and feeding/swallowing difficulties and help ensure children get adequate nutrition to meet their needs.
FNST is already available in six languages (English, Dutch, Swedish, Spanish, French, Persian) with three more languages (Polish, Spanish-Argentinian, Norwegian) will be coming soon. For those interested in this tool, start screening now by clicking on button below. Children identified as at risk would need to have a full nutritional or feeding assessment by the relevant health care professionals.
FNST News article
Nutricia launched the first scientifically validated online screening tool for children with cerebral palsy. Read the News article to get more background information on FNST and cerebral palsy in general.
Feeding and Nutrition Screening Tool (FNST) for children with cerebral palsy
Feature articles

The importance of nutritional support
Optimal nutritional support for a child with growth challenges will depend a lot on their age and their condition. Find out more about the importance and goals of nutritional support for these children. Read more on Danone Nutricia Research.

Nutritional solutions tailored to individual needs
Children with different growth challenges may have quite different nutritional requirements to each other. Their requirements often also depend on the age and weight of the child. Read more on Danone Nutricia Research.
- Beer et al. Nutr Clin Practice 2015;30:609-624
- Hecht et at. Clin Nutr 2013:34:53-59
- Curzon et al 2008
- Kogon et al 2008
- Wallace et al 2011
- Chang et al 2016
- El-Sherif et al 2012
- Galler et al 2012
- https://www.who.int/nutrition Jan 2020
- Vitrikas K, Dalton H, Breish D. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(4):213-20
- Clin Nutrition 2020
- Fung EB, Samson Fang L, Stallings VA, et al. J Am Diet Assoc 2002; 102: 361–73.
- Samson-Fang L, Fung E, Stallings VA, et al. J Pediatr 2002; 141: 637–43.
- Bell KL, Benfer KA, Ware RS, et al. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019;61(10):1175-81.
Are you a healthcare professional or (carer of) a diagnosed patient?
The product information for this area of specialization is intended for healthcare professionals or (carers of) diagnosed patients only, as these products are for use under healthcare professional supervision.
Please click ‘Yes’ if you are a healthcare professional or (carer of) a diagnosed patient, or ‘No’ to be taken to a full list of our products.
The information on this page is intended for healthcare professionals only.
If you aren't a healthcare professional, you can visit the page with general information, by clicking 'I'm not a healthcare professional' below.




